Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction to VAT Accounting in the UK
- 2 VAT Calculation: How it Works in the UK
- 2.1 Simple VAT Calculation Formula:
- 3 The Process of Filing a UK VAT Return
- 3.1 1. Gathering Records
- 3.2 2. Calculating Output Tax
- 3.3 3. Calculating Input Tax
- 3.4 4. Filling Out the VAT Return Form
- 3.5 5. Submitting & Paying
- 4 How VAT Registration and Exemptions Work in the UK
- 4.1 Understanding VAT Exemptions
- 5 Challenges in VAT Accounting and How to Overcome Them
- 5.1 VAT Accounting Challenges (And How to manage them)
- 5.1.1 1. Understanding Complex Rules
- 5.1.2 2. Determining the Correct VAT Rate
- 5.1.3 3. Accurate Record Keeping
- 5.1.4 4. Meeting Deadlines
- 5.1.5 5. MTD
- 5.1.6 6. International VAT Challenges
- 5.1.7 Conclusion
- 5.1.8 FAQs

Hassle free VAT accounting in UK
Introduction to VAT Accounting in the UK
VAT Accounting plays an important role in the UK tax system. VAT is considered a value-added tax. It is generally levied on most goods and services sold by businesses registered under VAT.
If your business is running in Uk you must understand VAT structure like how VAT works, and how to manage VAT accounting. If you understand the structure well, it helps you avoid fines.
In VAT accounting first, you have to collect VAT from your customers and forward it to HMRC. However, you can reclaim your VAT paid on eligible business-related purchases.
VAT Calculation: How it Works in the UK
VAT Rate differs depending on the types of services and goods you offer. Understanding this structure of how VAT calculation works is necessary.
Here are the main VAT rates in the UK:
|
VAT Rate |
Percentage |
Applies To |
|
Standard Rate |
20% |
Most goods and services |
|
Reduced Rate |
5% |
Used for Items like: Home energy, children’s car seats, mobility aids |
|
Zero Rate |
0% |
Applies to essentials: Food, books, children’s clothing, public transport |
Simple VAT Calculation Formula:
VAT = Net Price x VAT Rate
Example: If you sell a particular product at the price of £200 the standard VAT rate applies
(20%), the VAT amount is £200 × 20% = £40. The invoice is made of £240.
Accurate VAT calculation ensures your VAT return in the UK reflects correct figures. You are required to calculate how much VAT you’ve paid on your business purchases, this input tax can be reclaimed. The difference between what you owe and what you can claim back determines your final VAT position.
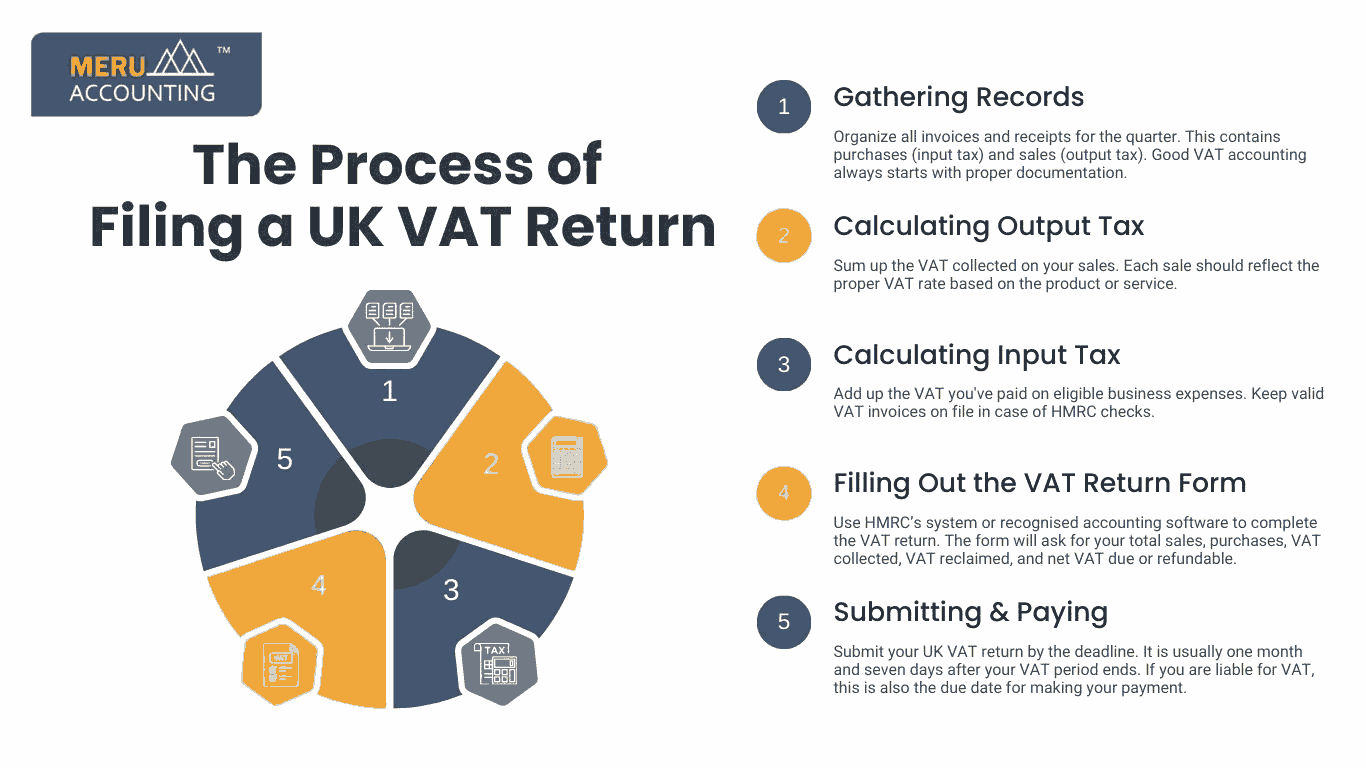
The Process of Filing a UK VAT Return
Filing a VAT return in the UK is a regular obligation for most businesses registered under VAT. The submission of VAT returns in the UK is done every quarter. It is done either through HMRC's online portal or supported software under the Making Tax Digital ( MTD) initiative.
Here’s a detailed process:
1. Gathering Records
Organize all invoices and receipts for the quarter. This contains purchases (input tax) and sales (output tax). Good VAT accounting always starts with proper documentation.
2. Calculating Output Tax
Sum up the VAT collected on your sales. Each sale should reflect the proper VAT rate based on the product or service.
3. Calculating Input Tax
Add up the VAT you've paid on eligible business expenses. Keep valid VAT invoices on file in case of HMRC checks.
4. Filling Out the VAT Return Form
Use HMRC’s system or recognised accounting software to complete the VAT return. The form will ask for your total sales, purchases, VAT collected, VAT reclaimed, and net VAT due or refundable.
5. Submitting & Paying
Submit your UK VAT return by the deadline. It is usually one month and seven days after your VAT period ends. If you are liable for VAT, this is also the due date for making your payment.
A mistake here can lead to penalties. That’s why many businesses use accounting software or professional services to manage this efficiently.
How VAT Registration and Exemptions Work in the UK
VAT registration in the UK depends on your business's taxable turnover. As of April 2024, the threshold for mandatory registration is £85,000. If your turnover goes over the limit, you must register. However, even if you're below this limit, voluntary registration can still be a smart move if you regularly incur VAT on expenses.
Understanding VAT Exemptions
Some goods and services are completely excluded from VAT These include:
- Financial services
- Health and medical services
- Education and training services
Unlike goods with Zero tax (which are taxable at 0%), exempt items are entirely outside the scope of VAT. Because of this, you can’t reclaim VAT on any expenses linked to those exempt activities. To keep your VAT accounting accurate, it’s important to understand the difference between zero-rated and non-taxable supplies. This helps ensure your VAT calculation is correct when filing your VAT return in the UK.
Challenges in VAT Accounting and How to Overcome Them
VAT Accounting Challenges (And How to manage them)
VAT accounting sounds simple, but Businesses often run into issues along their journey. Here are some of the challenges and solutions to overcome that:
1. Understanding Complex Rules
VAT regulations change often. Keeping up with them takes time and effort.
Solution: Subscribe to HMRC updates or consult a VAT expert to stay informed.
2. Determining the Correct VAT Rate
Products or services might fall into different rate categories or a mix of them.
Solution: Research carefully or get advice from professionals before applying rates in your VAT calculation.
3. Accurate Record Keeping
Poor records mean inaccurate returns and that can lead to penalties.
Solution: Use digital tools for real-time tracking and storage of invoices and receipts.
4. Meeting Deadlines
Missing the deadline for a UK VAT return is more common than you think.
Solution: Set automated calendar reminders and avoid last-minute filing.
5. MTD
All businesses registered under VAT adhere to making tax digital, which may feel challenging.
Solution: Use Making Tax Digital-approved software to handle VAT accounting and submission.
6. International VAT Challenges
Selling goods or services internationally introduces another layer of complexity.
Solution: Seek guidance on VAT treatment for imports, exports, and services outside the UK.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure of VAT Accounting is essential to stay compliant and avoid fines in the UK. From knowing how VAT calculation works to filing your UK VAT return correctly. Understanding each step and following each item is a key role for financial operations.
By addressing these challenges and using expert support, you can hassle out the process. At Accounts Junction, we make VAT accounting easy, giving you the freedom to focus on what you do best for smooth running your business.
FAQs
1. Who needs to register for VAT in the UK?
Any business with a taxable turnover over £85,000 must register. Voluntary registration is also possible below this threshold.
2. What are the VAT rates in the UK?
The standard rate is 20%, the reduced rate is 5%, and the zero rate is 0%, depending on the goods or services.
3. How often is a UK VAT return submitted?
Usually every quarter (every three months), but this may vary based on your VAT scheme.
4. What is the deadline for submitting a VAT return in the UK?
One month and seven days after the end of your VAT quarter.
5. What’s the difference between subject to zero VAT and exempt items?
Zero-rated items are taxable at 0% and allow input VAT recovery. Exempt items are outside VAT and don’t allow VAT recovery.
6. What is MTD?
A UK government initiative that requires businesses to keep digital records and file VAT returns through compatible software.
7. Can I reclaim VAT on my business purchases?
Yes, if you're VAT registered and the purchases relate to taxable business activities.
8. What happens if I miss my VAT return deadline?
HMRC may charge penalties or interest, depending on how late the return is.