What is Cash Accounting?
Cash accounting is a straightforward method where businesses record financial transactions only when cash is received or paid. Unlike accrual accounting, which records income and expenses when they are earned or incurred, cash accounting focuses solely on actual cash flow. This system is widely used by small businesses and sole proprietors due to its simplicity and ease of maintenance.
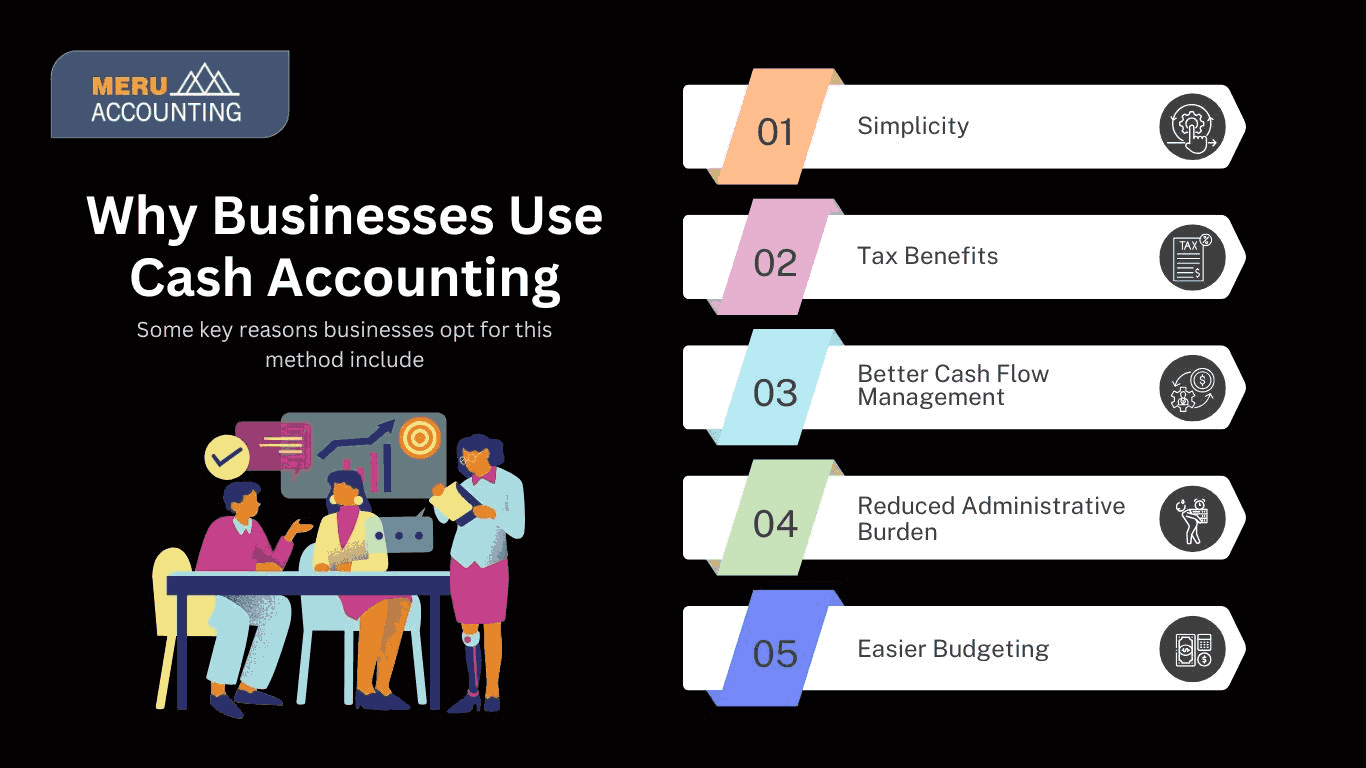
Why Businesses Use Cash Accounting
Many businesses prefer cash accounting because of its clarity and directness. Since transactions are recorded only when money exchanges hands, it provides a real-time picture of available cash. Some key reasons businesses opt for this method include:
- Simplicity: Minimal bookkeeping makes it easier to manage financial records. It eliminates tracking receivables and payables, reducing complexity.
- Tax Benefits: Taxes apply only to received income, helping businesses defer payments. This improves cash flow and reduces tax liability in slow periods.
- Better Cash Flow Management: Provides a clear view of available funds for better financial planning. Prevents cash shortages by focusing on actual cash transactions.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: No need to track invoices or deferred expenses, simplifying financial processes. Less paperwork leads to faster and more accurate reporting.
- Easier Budgeting: Since transactions are recorded when cash moves, businesses can budget based on real-time cash flow. This prevents overestimating income or underestimating expenses.
Cash vs Accrual Accounting: Key Differences
Understanding cash vs accrual accounting is essential for choosing the right method for a business. Here are the primary differences:
|
Feature |
Cash Accounting |
Accrual Accounting |
|
Revenue Recognition |
When cash is received |
When revenue is earned |
|
Expense Recording |
When cash is paid |
When expenses are incurred |
|
Complexity |
Simple and easy to manage |
More complex requires tracking receivables and payables |
|
Tax Implications |
Taxes paid only on received income |
Taxes apply to earned income, even if not yet received |
|
Financial Insight |
Reflects current cash flow |
Provides a clearer long-term financial picture |
|
Regulatory Compliance |
Not required for most small businesses |
Often required for tax and financial reporting |
|
Profitability Tracking |
Harder to measure profitability over time |
Provide a more accurate measure of long-term profitability |
|
Impact on Decision-Making |
Based on actual cash flow, limiting long-term planning |
Enables better strategic financial decisions based on complete data |
Pros and Cons of Cash Accounting
Before adopting cash accounting, businesses should understand its advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Simplifies Tax Filing: Since income is only recorded when received, tax calculations are straightforward, reducing the risk of overpaying taxes.
- Better for Cash-Dependent Businesses: Ideal for businesses that operate mostly with cash transactions, such as restaurants and retail stores.
- Easy to Implement: Requires little accounting knowledge or software. Suitable for small businesses and freelancers handling their own finances.
- Immediate Financial Tracking: Always shows actual cash available. Helps businesses react quickly to financial changes and unexpected expenses.
- Tax Timing Benefits: Income is taxed only when received, allowing better cash management. Businesses can defer tax payments to align with revenue flow.
Cons:
- Limited Credit Management: This does not track accounts receivable, making it difficult to manage customer credit efficiently.
- Harder to Secure Financing: Lenders and investors prefer accrual accounting for assessing business performance, potentially making it harder to obtain loans or investments.
- Limited Financial Insight: This does not account for unpaid invoices or future obligations. Can make long-term financial planning difficult.
- Not Suitable for Large Businesses: Larger businesses need accrual accounting for compliance and reporting. Investors and regulators often require more detailed financial records.
- Potential Cash Flow Mismanagement: Not tracking liabilities can cause unexpected shortages. Poor planning may lead to difficulties in meeting financial obligations.
Who Should use Cash Accounting?
Cash accounting is ideal for:
- Small businesses with simple transactions.
- Freelancers and sole proprietors managing personal finances.
- Businesses that don’t sell on credit or have high accounts receivable.
- Companies looking for an easy-to-use system with minimal record-keeping.
However, businesses with significant credit sales, multiple revenue streams, or compliance obligations may find accrual accounting more suitable.
Why Choose Our Accounting Services for Your Business?
Choosing the right accounting method is crucial for financial success. Our team specializes in cash vs. accrual accounting, helping businesses determine the best approach. We offer:
- Expert guidance to select the most efficient accounting system for your business. We assess your financial needs and recommend the best approach.
- Customized accounting solutions for small and medium businesses. Tailored services ensure streamlined bookkeeping and compliance.
- Reliable bookkeeping for accuracy and compliance. Helps businesses maintain precise records and avoid costly mistakes.
- Tax planning assistance to optimize financial performance. We help minimize tax liability and maximize savings.
- Financial reporting and analysis to provide valuable insights. We help businesses make informed decisions for growth and profitability.
- Audit support and compliance assistance to ensure businesses meet legal and financial regulations. Our team helps with audit preparation and accurate financial documentation.
- Scalable accounting solutions that grow with your business. We offer flexible services customized to evolving financial needs.
Whether you opt for cash accounting or need assistance transitioning to accrual accounting, our services ensure seamless financial management.
Conclusion
Cash accounting is a simple and effective method for businesses that deal primarily in cash transactions. It provides an easy way to track income and expenses while reducing administrative burdens. However, businesses with complex financial operations or significant credit sales may benefit more from accrual accounting. Understanding the differences between the two methods is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
At Account Junction, we provide expert accounting services customized to your business needs. Whether you require cash accounting, accrual accounting, or financial planning, our team ensures accuracy, compliance, and efficient bookkeeping.
FAQs
1. Is cash accounting suitable for all businesses?
- No, cash accounting works best for small businesses, freelancers, and sole proprietors with straightforward transactions.
2. Can I change the accounting method of my business from cash accounting to accrual accounting?
- Yes, businesses can transition to accrual accounting if they outgrow cash accounting. It may require adjustments and IRS approval for tax reporting.
3. What happens if my business grows and accrual accounting becomes necessary?
- Our experts can assist in making the switch smoothly, ensuring compliance and accurate financial reporting.
4. How do I know if cash accounting is right for my business?
- If your business mainly uses cash and does not offer credit to customers, cash accounting could work well for you.
5. Does using cash accounting simplify tax filing?
- Yes, since you only report income and expenses when cash is exchanged, tax calculations are more straightforward.